Published: 5 September 2019
Publications
Summary of spontaneous reports for meningococcal vaccines
Prescriber Update 40(3): 62-64
September 2019
Introduction
The Northland Meningococcal W vaccination programme started in December 2018 and ended in April 2019. This was a targeted programme, using meningococcal ACYW vaccines, to combat a community outbreak of meningococcal W disease in Northland. In addition, Bexsero (meningococcal B vaccine) was approved for use in New Zealand in July 2018.
Here we provide an overview of adverse reactions reported for these meningococcal vaccines between July 2018 and April 2019.
Spontaneous reports received between July 2018 and April 2019
The Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring (CARM) received 93 case reports of adverse events following immunisation (AEFI) for meningococcal vaccines between July 2018 and April 2019. There were 53 reports for meningococcal ACYW vaccines (Menactra and Nimenrix) and 46 reports for meningococcal B vaccine (Bexsero) during this time period. (Note some patients received more than one meningococcal vaccine so the number of case reports does not equal the sum of the vaccine reports.) Figure 1 shows the distribution of these reports over the time period.
Of the 93 reports, 92 were not serious and 1 was reported as life-threatening in a patient who had received Menactra (CARM ID 131300). The patient started to experience anaphylactic symptoms during the post-vaccination observation period, which the nurse promptly dealt with.
The most commonly reported reactions were injection site inflammation, arm pain and fever (Figure 2); these reactions are listed in the vaccine data sheets1–3. The largest number of reports were received for patients aged 17 years and younger (Figure 3) and from Northland (Figure 4). Reporting may have been higher in Northland due to the Meningococcal W outbreak vaccination programme. The Northland vaccination campaign was run from 5 December 2018 to 16 April 2019 and offered free meningococcal ACYW vaccinations to children aged 9 months to under 5 years and those aged 14 years to 19 years. It is not uncommon to see an increase in AEFI reports during mass vaccination campaigns or when new vaccines are introduced to the national immunisation schedule.
Figure 1: Number of reports* received by the Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring for meningococcal ACYW and B vaccines, July 2018–April 2019
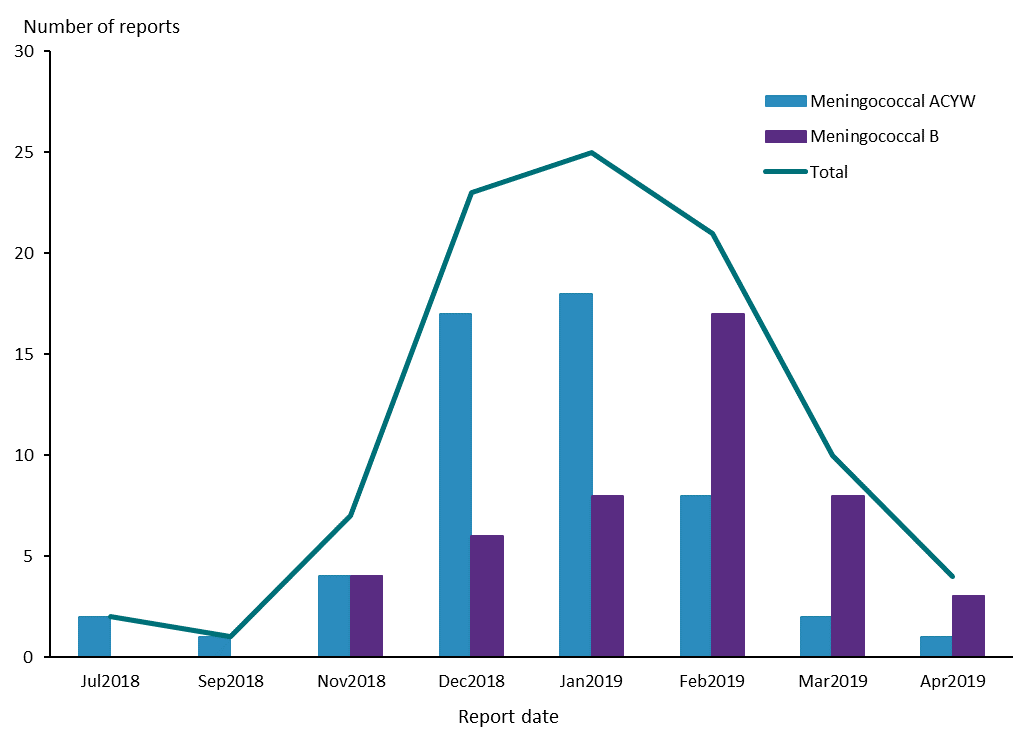
*. Some patients received more than one meningococcal vaccine so the total number of reports does not equal the sum of the meningococcal ACYW and B reports.
Source: Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring
Figure 2: Ten most frequently reported adverse reaction terms for meningococcal ACYW and B vaccines, July 2018–April 2019
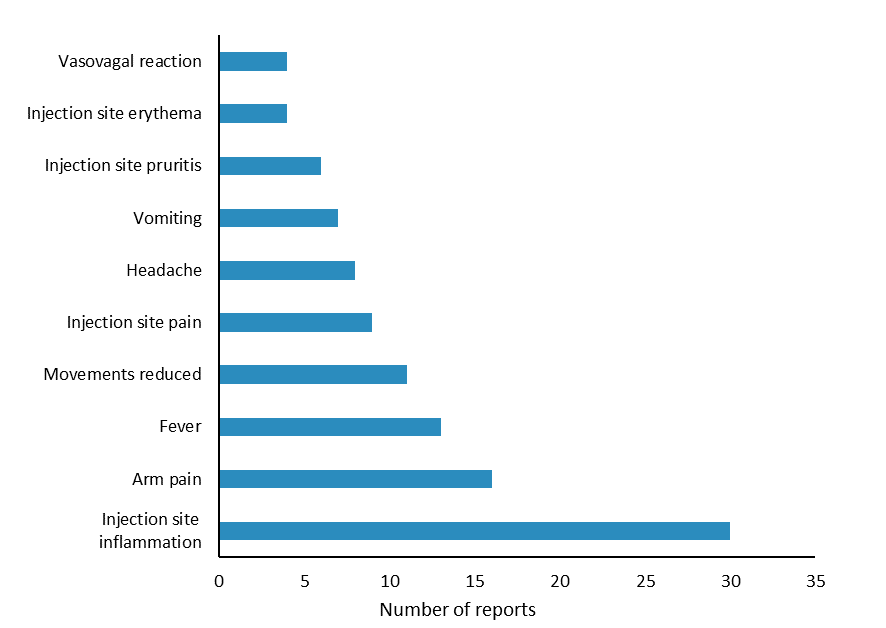
Source: Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring
Figure 3: Number of reports by age for adverse reactions to meningococcal ACYW and B vaccines, July 2018–April 2019
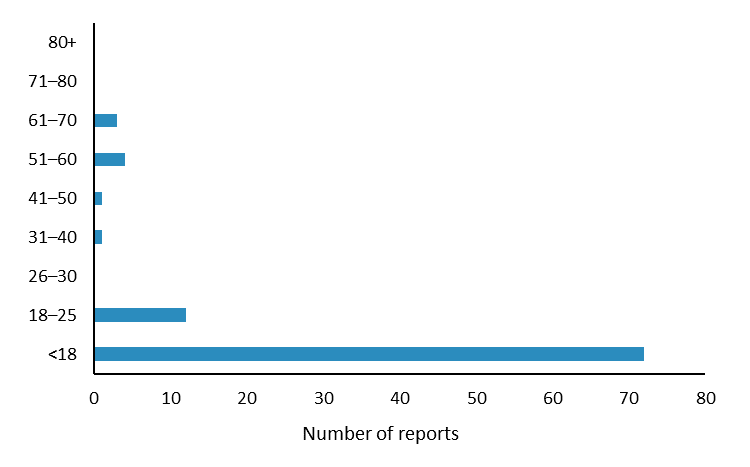
Source: Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring
Figure 4: Number of reports per region for adverse reactions to meningococcal ACYW and B vaccines, July 2018–April 2019
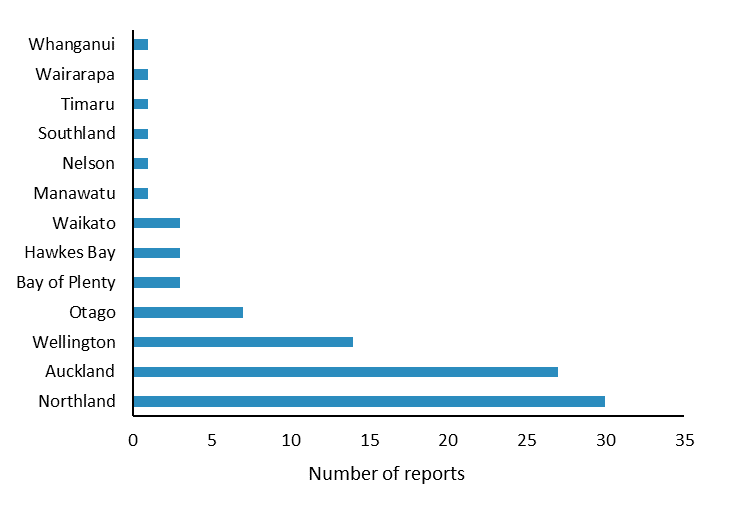
Source: Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring
References
- sanofi-aventis New Zealand Pty Ltd. 2018. Menactra New Zealand Data Sheet 5 July 2018. URL: www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/Datasheet/m/menactrainj.pdf (accessed 5 August 2019).
- Pfizer New Zealand Limited. 2019. Nimenrix New Zealand Data Sheet 12 January 2019. URL: www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/Datasheet/n/nimenrixinj.pdf (accessed 5 August 2019).
- GlaxoSmithKline NZ Limited. 2018. Bexsero New Zealand Data Sheet 12 October 2018. URL: www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/Datasheet/b/bexseroinj.pdf (accessed 5 August 2019).





