Published: 6 June 2024
Publications
Spotlight on cold and flu medicines containing pseudoephedrine
Published: 6 June 2024
Prescriber Update 45(2): 27–29
June 2024
Recently, Medsafe approved cold and flu medicines containing pseudoephedrine
under an expedited process. These medicines have not been available
in New Zealand for a number of years. This article is a reminder on
the use of cold and flu medicines containing pseudoephedrine and provides
information on how patients may obtain them.
What is pseudoephedrine?
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic used as a nasal decongestant.1,2 It provides short-term symptomatic relief of runny noses and nasal congestion due to conditions such as colds and flu.
Combination products contain pseudoephedrine with either paracetamol or ibuprofen, which relieve other cold and flu symptoms such as headache, body aches and fever. Some combination products also contain a sedating antihistamine to relieve sneezing, itchy or watery eyes and assist rest.
Use of pseudoephedrine
Cold and flu medicines containing pseudoephedrine can be used in adults and children aged 12 years and over. Advise patients of the following.
- Do not use more than one cold and flu medicine to avoid accidental overdose.
- Do not use in children aged under 12 years.
- Follow the recommended dose on the pack and do not exceed this dose.
When should pseudoephedrine be avoided?
Pseudoephedrine may exacerbate some existing medical conditions or increase the risk of adverse effects. Therefore, there are situations where the use of pseudoephedrine must or should be avoided, as outlined below.
Pseudoephedrine is contraindicated and must not be used in patients:1,2
- with uncontrolled hypertension or severe coronary artery disease
- taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or who have taken MAOIs within the previous 14 days
- with known hypersensitivity or idiosyncratic reaction to pseudoephedrine and any other ingredients in the medicine.
Use pseudoephedrine with caution in patients with hepatic or renal impairment, severe hepatic or renal dysfunction, controlled hypertension, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, coronary or ischaemic heart disease, glaucoma and enlarged prostate.1,2
Note that combination products have additional contraindications and cautions because they contain other active ingredients. Check the data sheets for full information.
Additionally, pseudoephedrine is included on the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) in-competition prohibited list.3 Athletes must stop taking pseudoephedrine at least 24 hours before competition.4
Other considerations for use
Other considerations for use of pseudoephedrine include the following.1,2
- Effects on sleep: Advise patients of sleeplessness if taken a few hours before going to bed. However, note that combination products containing a sedating antihistamine may cause drowsiness.
- Ischaemic colitis (reduced blood flow to the colon): Advise patients to discontinue use and seek medical advice if they develop sudden abdominal pain, rectal bleeding or other symptoms of ischaemic colitis.
- Skin reactions: Advise patients to discontinue use and seek medical advice if they develop a rash with or without fever or erythema (skin redness).
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy (PRES) or reversible cerebral vasoconstriction (RCVS): Advise patients to discontinue use and seek medical advice if they develop sudden onset of severe headache, nausea, vomiting and visual disturbances.
- Ischaemic optic neuropathy: Advise patients to discontinue use and seek medical attention if they experience a sudden loss of vision or decreased visual acuity, such as scotoma (a blind spot).
Check the data sheets for full information, particularly for combination products.
How can patients obtain these medicines?
Cold and flu medicines containing pseudoephedrine are classified as pharmacist-only medicines, meaning they can only be purchased after a consultation with a New Zealand-registered pharmacist. The pharmacist will advise if the medicine is clinically appropriate for the patient and the sale will be recorded.5
Where can I find more information?
For full prescribing information, check the data sheets for each product.
To find approved pseudoephedrine products, use Medsafe’s Product/Application Search.
- Select ‘Application search’ for the Search type.
- Enter ‘pseudoephedrine’ in the Ingredient field.
- Select ‘Provisional Consent (Section 23)’ from the Type dropdown box.
- Press Submit and the relevant products will be shown.
Figure 1 shows the Product/Application search webpage with relevant fields completed.
Figure 1: Screenshot of Medsafe’s Product/Application Search webpage* to find approved pseudoephedrine-containing medicines
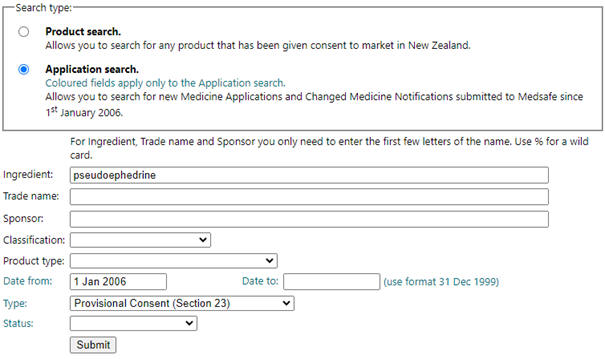
* URL: https://www.medsafe.govt.nz//DbSearch/
References
- Noumed Pharmaceuticals Limited. 2024. Noumed Decongestant Tablets New Zealand Data Sheet 26 March 2024. URL: www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/Datasheet/n/NoumedDecongestantTab.pdf (accessed 22 May 2024).
- JNTL Consumer Health (New Zealand) Limited. 2024. Sudafed Sinus and Nasal Decongestant New Zealand Data Sheet 12 April 2024. URL: www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/datasheet/s/SudafedSinusAndNasalDecongestanttab.pdf (accessed 22 April 2024).
- World Anti-Doping Agency. 2024. The Prohibited List. URL: www.wada-ama.org/en/prohibited-list (accessed 11 April 2024).
- World Anti-Doping Agency. 2021. TUE Physician Guidelines: Sinusitis/Rhinosinusitis version 2.0 November 2021 URL: www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/tue_physician_guidelines_sinusitis_rhinosinusitis.pdf (accessed 11 April 2024).
- Ministry of Health. 2024. Pseudoephedrine cold and flu medicines 15 April 2024. URL: www.health.govt.nz/our-work/regulation-health-and-disability-system/medicines-control/controlled-drugs/pseudoephedrine-cold-and-flu-medicines (accessed 22 April 2024).





